When working with MySQL databases in PHP, you often use functions like mysqli_query() or PDO::query() to fetch data. Behind the scenes, these functions can retrieve query results in two different ways: buffered or unbuffered.
Understanding the difference is crucial for performance, especially when working with large datasets. Let’s break it down.
What Are Buffered Queries?
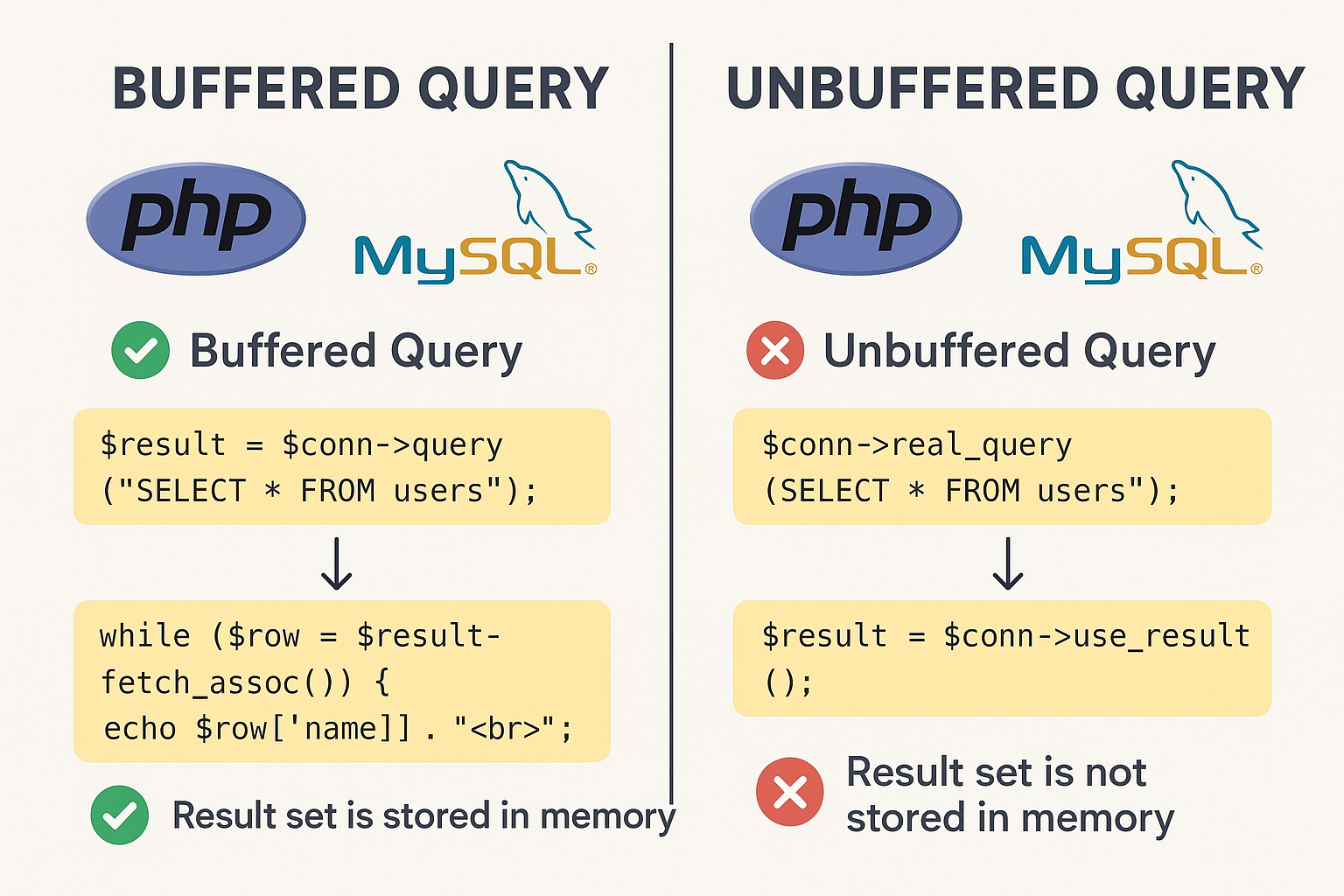
A buffered query means that PHP fetches and stores (buffers) the entire result set from the MySQL server into memory as soon as the query is executed.
-
This is the default behavior for most PHP MySQL extensions.
-
Once buffered, you can iterate through the result set multiple times.
-
The connection to the MySQL server is freed up immediately after fetching.
Example (Buffered Query using mysqli_query)
What Are Unbuffered Queries?
Unbuffered queries can also be referred to as “use result”.
<?php
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "testdb");
// First send the query
$conn->real_query("SELECT * FROM users");
// Use unbuffered result
$result = $conn->use_result();
while ($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo $row['name'] . "<br>";
}
$result->free();
$conn->close();
?>
Or you can use MYSQLI_USE_RESULT flag in the query() method:
<?php
$mysqli = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "testdb");
$result = $mysqli->query("SELECT Name FROM City", MYSQLI_USE_RESULT);
if ($result) {
while ($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo $row['Name'] . PHP_EOL;
}
}
$result->close();
?>
Alternatively, with PDO you can disable buffering:
How to Turn on Unbuffered Query In Laravel
Inside of config/database.php file add a new connection or alter the existing connection for mysql, with the connection’s options array set PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_USE_BUFFERED_QUERY to false.
// config/database.php
'connections' => [
// ... other connections
'mysql_unbuffered' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'host' => env('DB_HOST', '127.0.0.1'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT', '3306'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE', 'forge'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME', 'forge'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD', ''),
'unix_socket' => env('DB_SOCKET', ''),
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
'collation' => 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci',
'prefix' => '',
'prefix_indexes' => true,
'strict' => true,
'engine' => null,
'options' => [
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_USE_BUFFERED_QUERY => false,
],
],
],
To use the unbuffered connection for specific queries:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
// ...
$results = DB::connection('mysql_unbuffered')->table('large_table')->cursor();
foreach ($results as $row) {
// Process each row without loading the entire result set into memory
}
🔹 Conclusion
-
Buffered queries are convenient for small or moderate datasets because they free up the MySQL connection quickly and allow multiple passes over the result set.
-
Unbuffered queries are ideal for very large datasets where memory usage is a concern, but you lose some flexibility.